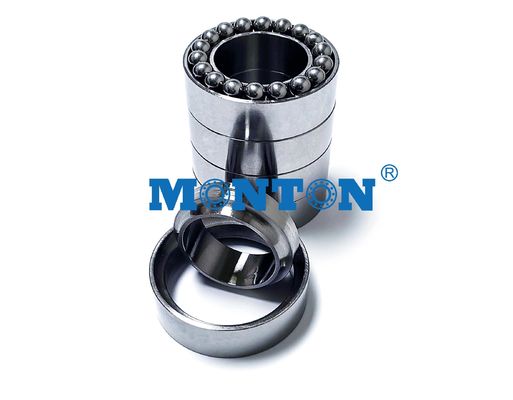
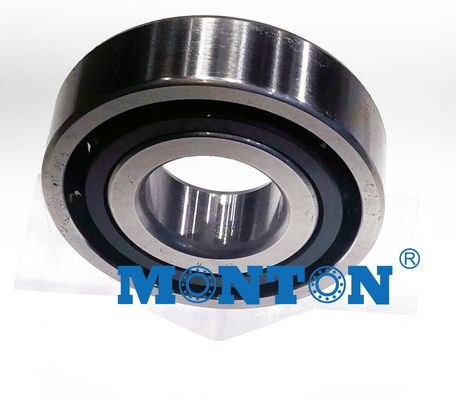
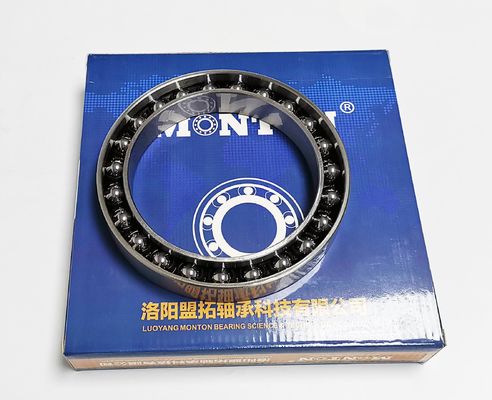
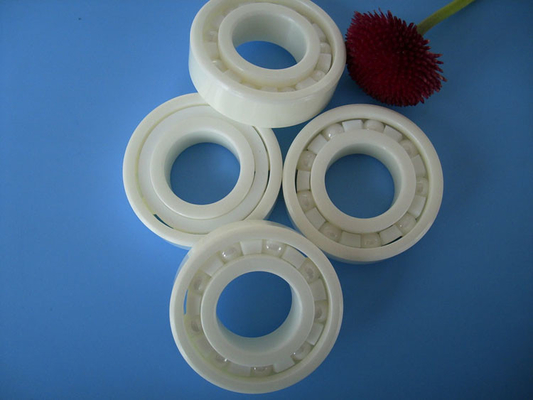
Full Ceramic Bearings have races and balls that are made entirely of ceramic material and are superior to common steel bearings in many ways. Ceramic is the perfect material for any application seeking to achieve higher RPM’s, reduce overall weight or for extremely harsh environments where high temperatures and corrosive substances are present.
Full Ceramic Bearings are usually made of following materials:
- Silicon Nitride (SiN4)
- Alumina Oxide (Al2O3)
- Zirconia Oxide (ZrO2)
- Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Full Ceramic Bearing Benefits
- Will not corrode or rust
- 2/3 the weight of steel
- Resistant to resist acids, alkali, blood, salt and water
- Extremely low coefficient of friction and thermal expansion
- Lower friction results in less energy consumed
- Operating Temperature from as low as (-85°C) up to (+ 900°C)
Full Ceramic Bearing Applications
Full Ceramic bearings are used in specialty applications like chemical baths, vacuum environments, semiconductor manufacturing, food processing industries, radiotherapy, MRI, patient positioning systems and more. Any extreme environment that requires non-corrosive, non-conductive or non-magnetic bearings is ideal for full ceramic bearings.
Because ceramic is a glass like surface it has an extremely low coefficient of friction and is ideal for applications seeking to reduce friction. Ceramic balls require less lubrication and have a greater hardness than steel balls which will contribute to increased bearing life. Thermal properties are better than steel balls resulting in less heat generation at high speeds.
Radial Full Ceramic Bearings
Full Ceramic Bearings are made entirely of ceramic material and are superior to common steel bearings in many ways. Ceramic is the perfect material for any application seeking to achieve higher RPM's, reduce overall weight or for extremely harsh environments where high temperatures and corrosive substances are present.
Applications such as cryopumps, medical devices, semiconductors, machine tools, turbine flow meters, food processing equipment, robotics and optics. Ceramic materials commonly used for bearings are Silicon Nitride (Si3N4), Zirconia Oxide (ZrO2), Alumina Oxide (Al2O3) or Silicon Carbide (SiC.)
Because ceramic is a glass like surface it has an extremely low coefficient of friction and is ideal for applications seeking to reduce friction. Ceramic balls require less lubricant and have a greater hardness than steel balls which will contribute to increased bearing life. Thermal properties are better than steel balls resulting in less heat generation at high speeds. Full Ceramic bearings can have a retainer or full complement of balls, retainer materials used are PEEk and PTFE.
Full ceramic bearings can continue to operate under extremely high temperatures and are capable of operating up to 1800 Deg. F. Ceramic is much lighter than steel and many bearings are 1/3 the weight of a comparable steel bearing. Full ceramic bearings are highly corrosion resistant and will stand up to most common acids, they will not corrode in exposure to water or salt water. And finally full ceramic bearings are non-conductive.
The purpose of a radial bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support loads. This is achieved by using two races to hold the balls and to spread the load through the balls. As the bearing race rotates it causes the balls to rotate. The ball provides for substantially less rolling resistance and coefficient of friction than if two flat surfaces were rotating.
| 6000CE |
6200CE |
6300CE |
ZrO2 6000 |
ZrO2 6200 |
ZrO2 6300 |
Si3N4 6000 |
Si3N4 6200 |
Si3N4 6300 |
| 6001CE |
6201CE |
6301CE |
ZrO2 6001 |
ZrO2 6201 |
ZrO2 6301 |
Si3N4 6001 |
Si3N4 6201 |
Si3N4 6301 |
| 6002CE |
6202CE |
6302CE |
ZrO2 6002 |
ZrO2 6202 |
ZrO2 6302 |
Si3N4 6002 |
Si3N4 6202 |
Si3N4 6302 |
| 6003CE |
6203CE |
6303CE |
ZrO2 6003 |
ZrO2 6203 |
ZrO2 6303 |
Si3N4 6003 |
Si3N4 6203 |
Si3N4 6303 |
| 6004CE |
6204CE |
6304CE |
ZrO2 6004 |
ZrO2 6204 |
ZrO2 6304 |
Si3N4 6004 |
Si3N4 6204 |
Si3N4 6304 |
| 6005CE |
6205CE |
6305CE |
ZrO2 6005 |
ZrO2 6205 |
ZrO2 6305 |
Si3N4 6005 |
Si3N4 6205 |
Si3N4 6305 |
| 6006CE |
6206CE |
6306CE |
ZrO2 6006 |
ZrO2 6206 |
ZrO2 6306 |
Si3N4 6006 |
Si3N4 6206 |
Si3N4 6306 |
| 6007CE |
6207CE |
6307CE |
ZrO2 6007 |
ZrO2 6207 |
ZrO2 6307 |
Si3N4 6007 |
Si3N4 6207 |
Si3N4 6307 |
| 6008CE |
6208CE |
6308CE |
ZrO2 6008 |
ZrO2 6208 |
ZrO2 6308 |
Si3N4 6008 |
Si3N4 6208 |
Si3N4 6308 |
| 6009CE |
6209CE |
6309CE |
ZrO2 6009 |
ZrO2 6209 |
ZrO2 6309 |
Si3N4 6009 |
Si3N4 6209 |
Si3N4 6309 |
| 6010CE |
6210CE |
6310CE |
ZrO2 6010 |
ZrO2 6210 |
ZrO2 6310 |
Si3N4 6010 |
Si3N4 6210 |
Si3N4 6310 |
| 6011CE |
6211CE |
6311CE |
ZrO2 6011 |
ZrO2 6211 |
ZrO2 6311 |
Si3N4 6011 |
Si3N4 6211 |
Si3N4 6311 |
| 6012CE |
6212CE |
6312CE |
ZrO2 6012 |
ZrO2 6212 |
ZrO2 6312 |
Si3N4 6012 |
Si3N4 6212 |
Si3N4 6312 |
| 6013CE |
6213CE |
6313CE |
ZrO2 6013 |
ZrO2 6213 |
ZrO2 6313 |
Si3N4 6013 |
Si3N4 6213 |
Si3N4 6313 |
| 6014CE |
6214CE |
6314CE |
ZrO2 6014 |
ZrO2 6214 |
ZrO2 6314 |
Si3N4 6014 |
Si3N4 6214 |
Si3N4 6314 |
| 6015CE |
6215CE |
6315CE |
ZrO2 6015 |
ZrO2 6215 |
ZrO2 6315 |
Si3N4 6015 |
Si3N4 6215 |
Si3N4 6315 |
| 6016CE |
6216CE |
6316CE |
ZrO2 6016 |
ZrO2 6216 |
ZrO2 6316 |
Si3N4 6016 |
Si3N4 6216 |
Si3N4 6316 |
| 6017CE |
6217CE |
6317CE |
ZrO2 6017 |
ZrO2 6217 |
ZrO2 6317 |
Si3N4 6017 |
Si3N4 6217 |
Si3N4 6317 |
| 6018CE |
6218CE |
6318CE |
ZrO2 6018 |
ZrO2 6218 |
ZrO2 6318 |
Si3N4 6018 |
Si3N4 6218 |
Si3N4 6318 |
| 6019CE |
6219CE |
6319CE |
ZrO2 6019 |
ZrO2 6219 |
ZrO2 6319 |
Si3N4 6019 |
Si3N4 6219 |
Si3N4 6319 |
| 6020CE |
6220CE |
6320CE |
ZrO2 6020 |
ZrO2 6220 |
ZrO2 6320 |
Si3N4 6020 |
Si3N4 6220 |
Si3N4 6320 |
Single-row, deep groove radial ball bearings are the most common bearing type, having a wide range of applications. Radial bearings are made with very high levels of precision and used in applications where rotational performance and low torque is necessary, but load is a secondary issue. Deep-groove bearings however do have higher load ratings for their size than shallow-groove ball bearings, but are also less tolerant of misalignment.
Ceramic hybrid ball bearings use ceramic balls. Ceramic balls weigh up to 40% less than steel balls, depending on size. This reduces centrifugal loading and skidding, so hybrid ceramic bearings can operate up to 50% faster than conventional bearings. This means that the outer race groove exerts less force inward against the ball as the bearing spins. This reduction in force reduces the friction and rolling resistance. The lighter ball allows the bearing to spin faster, and uses less energy to maintain its speed. Ceramic hybrid ball bearings use these ceramic balls in place of steel balls. They are constructed with steel inner and outer rings, but ceramic balls so they are known as hybrids.


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 












