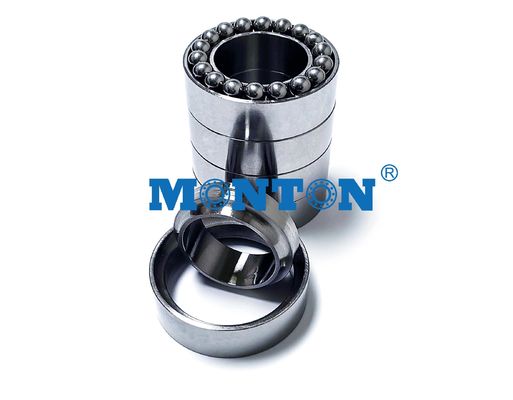
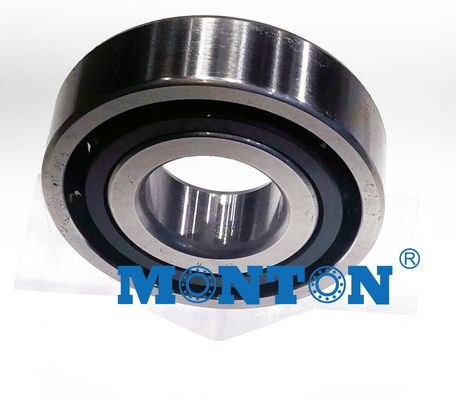
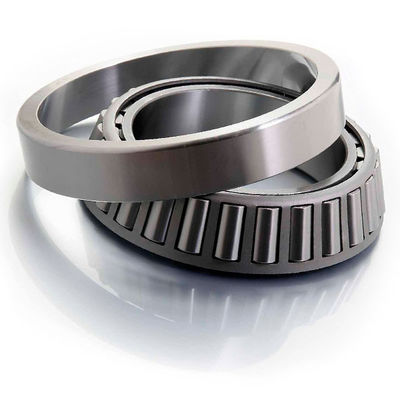
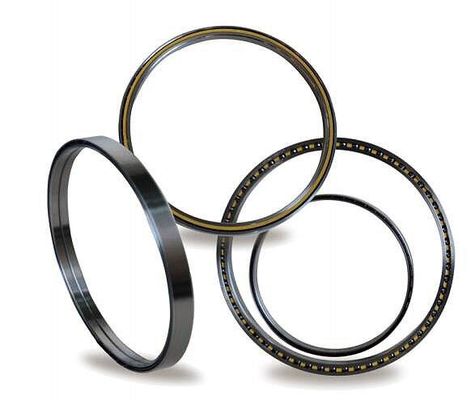
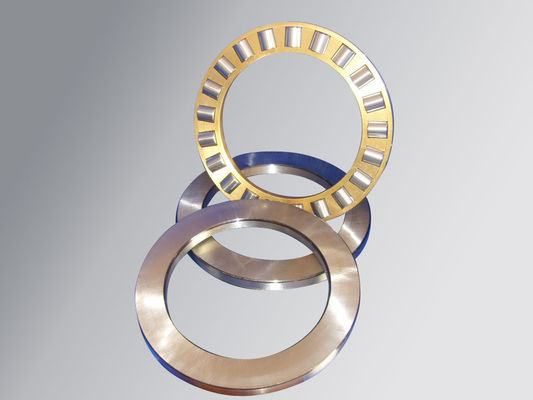
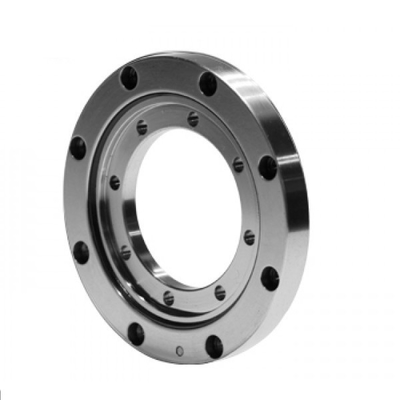
Features of the Crossed Roller Ring

Structure and Features
With the Cross-Roller Ring, cylindrical rollers are arranged with each roller perpendicular to the adjacent roller, in a 90° V groove, separated from each other by a spacer retainer. This design allows just one bearing to receive loads in all directions including radial, axial and moment loads. Since the Cross-Roller Ring achieves high rigidity despite the minimum possible dimensions of the inner and outer rings, it is optimal for applications such as joints and swiveling units of industrial robots, swiveling tables of machining centers, rotary units of manipulators, precision rotary tables, medical equipment, measuring instruments and IC manufacturing machines.
High Rotation Accuracy
The spacer retainer fitting among cross-arrayed rollers prevents rollers from skewing and the rotational torque from increasing due to friction between rollers. Unlike conventional types using steel sheet retainers, the Cross-Roller Ring does not cause unilateral contact of roller or seize. Thus, even under a preload, the Cross-Roller Ring provides stable rotation.
Since the inner and outer rings are designed to be separable, the bearing clearance can be adjusted.
In addition, a preload can be applied. These features enable accurate rotation.
Easy Handling
The inner and outer rings, which are separable, are secured to the Cross-Roller Ring body after being installed with rollers and spacer retainers in order to prevent the rings from separating from each other. Thus, it is easy to handle the rings when installing the Cross-Roller Ring.
Skewing Prevention
The spacer retainer keeps rollers in their proper position, thereby preventing them from skewing(tilted rollers). This eliminates friction between rollers, and therefore secures a stable rotational torque.
Increased Rigidity (Three to Four Times Greater than the Conventional Type) Unlike the thin angular ball bearings installed in double rows, the cross array of rollers allows a single Cross-Roller Ring unit to receive loads in all directions, increasing the rigidity to three to four times greater than the conventional type.

Large Load Capacity
(1) Compared with conventional steel sheet retainers, the spacer retainer allows a longer effective
contact length of each roller, thus signifi cantly increasing the load capacity. The spacer retainer guides rollers by supporting them over the entire length of each roller, whereas the conventional type of retainer supports them only at a point at the center of each roller. Such one-point contact cannot suffi ciently prevent skewing.

(2) In conventional types, the loaded areas are asymmetrical between the outer ring and the inner ring sides around the roller longitudinal axis. The greater the applied load is, the greater the moment becomes, leading end-face contact to occur. This causes frictional resistance, which hinders smooth rotation and quickens wear.


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 












